Accounting systems and assumptions are different; beliefs about the role of regulation, executives' families, business partnerships and the like. There is a reason why virtually all of the companies currently being forcibly removed from the listing of US stock exchanges are Chinese, but questions about cultural as well as organizational and financial structures remain uncertain.
That said, China has now surpassed the US as the largest internet market. That is not necessarily the same thing as the most valuable, however that might be measured, but it probably suggests that the one will follow the other at some point. Tencent, one of the Chinese internet behemoths, is a big part of that story. The question, however, is what that means to investors, suppliers, non-Chinese customers and regulators, especially those based outside of mainland China.
And that is what makes the process of valuation so challenging. As the following article explains, Tencent has an effective business model: it owns QQ and WeChat, using them effectively as free services on which over a billion customers can then buy products and services. Questions remain about the veracity of its reporting and even the meaning of some of the numbers. This is not necessarily a criticism but almost more of a social commentary. Without transparent and comparable data, it is hard to accurately discern strengths from weaknesses.
China is going to remain an economic force no matter how many ups and downs it endures. Welcome to our world, as the saying goes. But until those inside and outside these evolving technological and geographic circles are better able to communicate their assumptions and interpretations, a tremendous amount of value will be debated and possibly lost by everyone interested. JL
The Economist reports:
Is TENCENT one of the world’s greatest internet firms?
IS TENCENT one of the world’s greatest internet firms? There are grounds for scepticism. The Chinese gaming and social-media firm started in the same way many local internet firms have: by copying Western success. QQ, its instant-messaging service, was a clone of ICQ, an Israeli invention acquired by AOL of America. And unlike global internet giants such as Google and Twitter, Tencent still makes its money in its protected home market.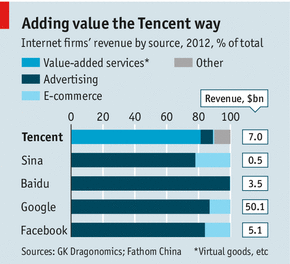
Yet the Chinese firm’s stockmarket valuation briefly crossed the $100 billion mark for the first time. Given that the valuation of Facebook, the world’s leading social-media firm, itself crossed that threshold only a few weeks ago, it is reasonable to wonder whether Tencent is worth so much. However, Tencent now has bigger revenues and profits than Facebook. In the first half of this year Tencent enjoyed revenues of $4.5 billion and gross profits of $2.5 billion, whereas Facebook saw revenues of $3.3 billion and gross profits of $935m.
The Chinese firm’s market value reflects the phenomenal rise in its share price. A study out this week from the Boston Consulting Group found that Tencent had the highest shareholder total return (share-price appreciation plus dividends) of any large firm globally from 2008 to 2012—topping Amazon and even Apple. Tencent has created a better business model than its Western peers. Many internet firms build a customer base by giving things away, be they search results or social-networking tools. They then seek to monetise their users, usually turning to online advertising. Google is a glorious example. Other firms try to make e-commerce work. But as the case of revenue-rich but profit-poor Amazon suggests, this can also be a hard slog.
Tencent does give its services away: QQ is used by 800m people, and its WeChat social-networking app (which initially resembled America’s WhatsApp) has several hundred million users. What makes it different from Western rivals is the way it uses these to peddle online games and other revenue-raising offerings.
Once users are hooked on a popular game, Tencent then persuades them to pay for “value-added services” such as fancy weapons, snazzy costumes for their avatars and online VIP rooms. Whereas its peers are still making most of their money from advertising, Fathom China, a research firm, reckons Tencent gets 80% of its revenues from such kit (see chart).
This year China has overtaken America to become the world’s biggest e-commerce market, in terms of sales. It is also now the biggest market for smartphones. This means it may soon have the world’s dominant market in “m-commerce”, purchases on mobile devices.
Tencent’s main rivals in Chinese m-commerce are Baidu, which dominates search on desktop computers (helped by the government’s suppression of Google) and Alibaba, an e-commerce giant now preparing for a huge share offering. All three have gone on acquisition sprees, in an attempt to lead the market. The big worry for investors is the cost of this arms race.
Alibaba recently invested $300m in AutoNavi, an online-mapping firm, and nearly $600m in Sina Weibo, China’s equivalent of Twitter. Baidu has been even more ambitious, spending $1.85 billion to buy 91 Wireless, the country’s biggest third-party store for smartphone apps, and $370m for PPS, an online-video firm.
Tencent may have an edge over its two rivals in m-commerce because of the wild popularity of WeChat, which is used on mobile phones. But to ensure it stays in the race, it is also spending heavily. On September 16th it said it will spend $448m to acquire a big stake in Sogou, an online-search firm; it plans to merge its own flagging search engine (aptly named Soso) into the venture. It had previously invested in Didi Dache, China’s largest taxi-hailing app, and is rumoured to be interested in online travel and dating firms too.
The three Goliaths are buying up innovative firms because they are too big and bureaucratic to create things themselves, mutter some entrepreneurs (presumably not those being bought out handsomely). A more pressing worry for Tencent’s shareholders is that its lavish spending, on top of heavy investment in improving its unimpressive e-commerce offerings, will eat into profits. Worse, the m-commerce arms race risks distracting it from gaming and value-added services, the cash cows that are paying for everything else. A $100 billion valuation might then seem too rich.




















0 comments:
Post a Comment